
Best GME Professional in-Circuit ESR Review gme Buying Guide
Best GME Professional In-Circuit ESR Review & Buying Guide
Navigating the world of electronics repair and troubleshooting can feel like traversing a dense jungle. Buried deep within circuits, seemingly innocuous components can harbor hidden faults, silently crippling entire systems. One of the most common culprits? Failing capacitors, often signaled by an elevated Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR). Identifying these faulty capacitors quickly and accurately is paramount for efficient repair work, and that’s where a dedicated in-circuit ESR meter becomes an indispensable tool. Among the available options, GME professional ESR meters stand out for their reliability, accuracy, and ease of use, making them a popular choice for both seasoned professionals and enthusiastic hobbyists. This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of GME professional in-circuit ESR meters, exploring their features, benefits, and helping you choose the best model for your specific needs. We’ll examine the nuances of ESR measurement, discuss practical applications, and provide essential tips for maximizing the effectiveness of your chosen GME ESR meter.
Understanding ESR and Its Importance
Equivalent Series Resistance, or ESR, is a critical parameter that indicates the internal resistance of a capacitor. Ideally, a capacitor should only exhibit capacitive reactance, but in reality, all capacitors have some inherent resistance due to the materials and construction used. As capacitors age, degrade, or are subjected to harsh operating conditions, their ESR tends to increase. This increased ESR can manifest in a variety of problems, from reduced circuit performance and increased heat dissipation to complete circuit failure. High ESR effectively turns the capacitor into a resistor, impeding its ability to store and release energy efficiently. Identifying capacitors with elevated ESR early on can prevent cascading failures and save considerable time and money in repair work. Think of it like detecting a small leak in a dam before it turns into a catastrophic breach. A GME professional in-circuit ESR meter allows you to diagnose these “leaks” without the need to desolder components, saving valuable time and minimizing the risk of damage to the surrounding circuitry. This is especially crucial in densely populated circuit boards where removing components can be a delicate and time-consuming process.
Why is in-circuit testing so important? Because desoldering a capacitor to test it out-of-circuit can be problematic. The desoldering process itself can stress the capacitor, potentially altering its ESR and leading to inaccurate readings. Furthermore, the act of removing and reinstalling components carries the risk of damaging the PCB traces or pads, especially on older or more fragile boards. In-circuit testing avoids these pitfalls, allowing you to assess the capacitor’s ESR under its normal operating conditions, providing a more realistic and reliable indication of its health. For example, consider a power supply in a vintage audio amplifier. The filter capacitors in the power supply are crucial for maintaining stable voltage rails. If these capacitors have high ESR, they will struggle to filter out ripple, leading to hum or distortion in the audio output. Using a GME professional ESR meter, you can quickly check the ESR of these capacitors in-circuit without having to dismantle the entire power supply, pinpointing the faulty component and restoring the amplifier to its former glory.
Moreover, understanding the typical ESR values for different types of capacitors is crucial for accurate diagnosis. Electrolytic capacitors, for instance, generally have higher ESR values than ceramic or film capacitors. A GME professional ESR meter, often equipped with built-in capacitor type selection, helps you interpret readings accurately by providing reference values for various capacitor types and capacitance values. Therefore, having a clear understanding of ESR and utilizing a reliable GME professional ESR meter are essential for efficient and effective electronics troubleshooting and repair.
Key Features to Consider in a GME Professional ESR Meter
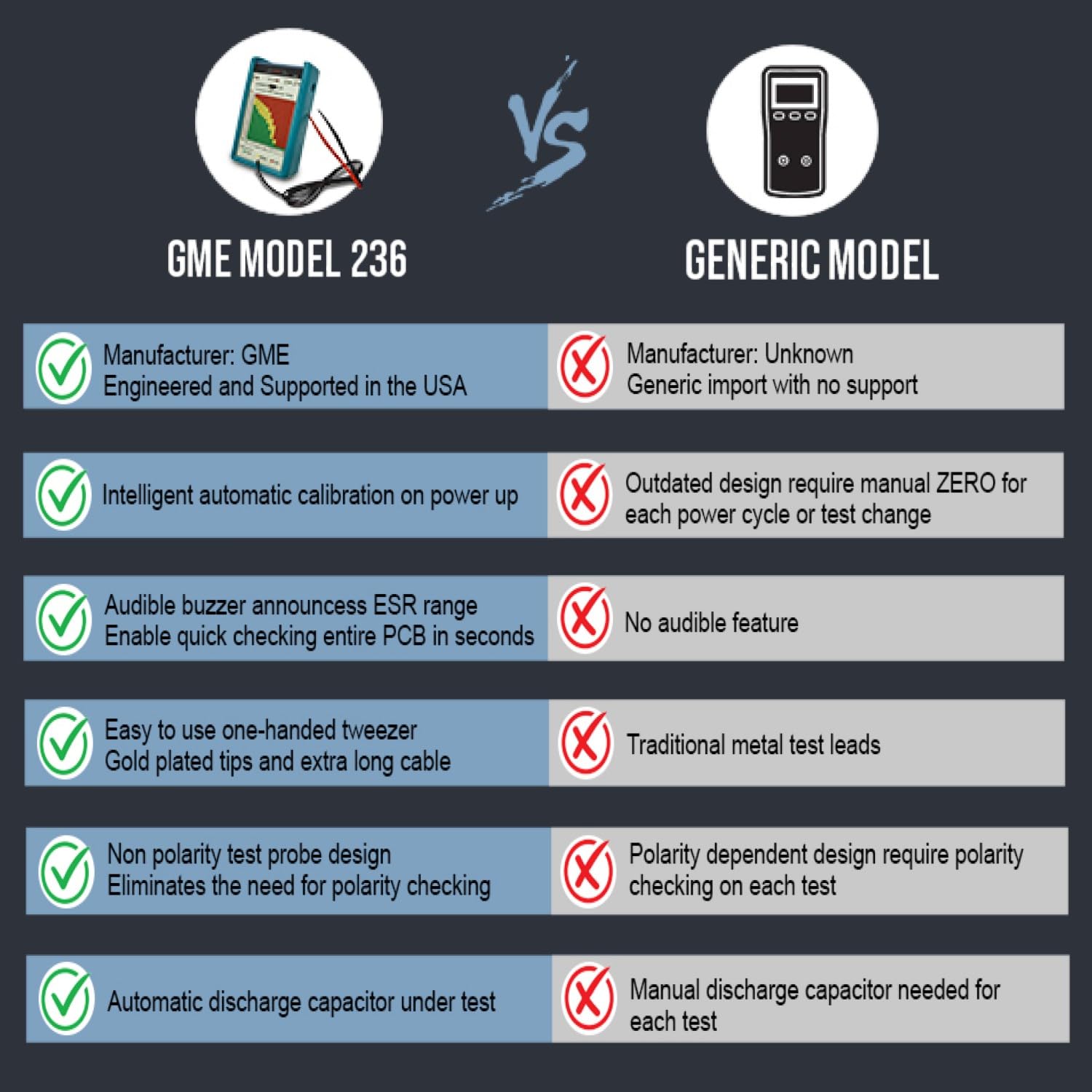
Choosing the right GME professional ESR meter requires careful consideration of several key features to ensure it meets your specific needs and budget. Accuracy is paramount. Look for meters that boast high accuracy specifications, typically expressed as a percentage plus a fixed value (e.g., ±1% + 0.01Ω). This specification indicates the potential error range in the ESR measurement. The lower the percentage and the fixed value, the more accurate the meter. Resolution is another important factor, referring to the smallest change in ESR that the meter can detect. A higher resolution allows you to identify subtle changes in ESR, which can be crucial for diagnosing capacitors that are nearing the end of their lifespan. For example, a meter with a resolution of 0.001Ω can detect smaller changes in ESR compared to a meter with a resolution of 0.01Ω.
Frequency of operation also plays a significant role. ESR varies with frequency, so it’s important to choose a meter that operates at a frequency suitable for the types of capacitors you’ll be testing. Many GME professional ESR meters operate at frequencies between 100 kHz and 1 MHz, which is generally considered optimal for testing electrolytic capacitors. However, for testing smaller capacitors or capacitors used in high-frequency circuits, a meter with a higher operating frequency may be necessary. In-circuit testing capability is a must. Ensure that the meter is specifically designed for in-circuit testing, as this will allow you to measure ESR without desoldering components. A good in-circuit ESR meter will use a low test voltage to avoid turning on semiconductors in the circuit under test, preventing inaccurate readings or damage to the components. Probe quality and design are often overlooked but are critical for accurate measurements. Look for meters that come with high-quality probes with sharp tips that can easily make contact with small test points on a PCB. The probe cables should also be shielded to minimize noise and interference.
Beyond the core technical specifications, consider user-friendliness. A clear and easy-to-read display is essential, especially in dimly lit environments. Some GME professional ESR meters feature backlit LCD screens, which improve visibility. Ease of operation is also important. Look for meters with intuitive controls and a simple user interface. Some meters also offer features such as auto-ranging, which automatically selects the appropriate measurement range, and data hold, which allows you to freeze the reading on the display for easier recording. Finally, consider the meter’s durability and build quality. A well-built meter will withstand the rigors of daily use and last for many years. Look for meters with rugged enclosures and robust construction. Some meters also come with protective cases to prevent damage during transport and storage. When considering your next gme tool, give these feature careful thought.
Comparing Popular GME Professional In-Circuit ESR Meter Models
The market offers a range of GME professional in-circuit ESR meters, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Let’s compare a few popular models to highlight their key features and help you make an informed decision.
| Model | ESR Range | Accuracy | Test Frequency | Display | Power Source | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GME ESR-100 | 0.001Ω – 100Ω | ±1% + 0.01Ω | 100 kHz | LCD with Backlight | 9V Battery | Auto Ranging, Data Hold, Audible Alert |
| GME ESR-200 | 0.001Ω – 200Ω | ±0.5% + 0.005Ω | 100 kHz / 1 MHz | LCD with Backlight | 9V Battery / AC Adapter | Auto Ranging, Data Hold, Audible Alert, Capacitor Type Selection |
| GME ESR-300 | 0.0001Ω – 100Ω | ±0.2% + 0.001Ω | 100 kHz | OLED with Backlight | Rechargeable Battery | Auto Ranging, Data Hold, Audible Alert, Capacitor Type Selection, Bluetooth Connectivity |
The GME ESR-100 is a solid entry-level option, offering a good balance of accuracy and affordability. It’s suitable for general-purpose ESR testing and is easy to use, making it a good choice for beginners. However, it lacks advanced features such as capacitor type selection and multiple test frequencies. The GME ESR-200 steps up the game with improved accuracy and the addition of a 1 MHz test frequency, making it more versatile for testing a wider range of capacitors. It also includes capacitor type selection, which simplifies the interpretation of ESR readings. This model is a good choice for intermediate users who need more advanced features but don’t want to break the bank. The GME ESR-300 is the top-of-the-line model, boasting the highest accuracy and resolution, as well as a vibrant OLED display and Bluetooth connectivity. It also features a rechargeable battery, eliminating the need for disposable batteries. This model is ideal for professionals who demand the highest possible accuracy and features and are willing to pay a premium. Consider your budget and the types of capacitors you’ll be testing most frequently when making your decision. Don’t overspend on features you don’t need, but also don’t skimp on accuracy if you’re working on critical applications. For those looking for high precision when evaluating gme parts, the ESR-300 would be the best option.
Let’s consider a real-world scenario. Imagine you’re repairing a vintage computer with numerous electrolytic capacitors on the motherboard. Some of these capacitors may have degraded over time, causing instability or malfunctions. Using a GME ESR-100, you can quickly check the ESR of these capacitors in-circuit. If you find a capacitor with an ESR significantly higher than the expected value, you can replace it, restoring the computer to its original performance. Now, imagine you’re working on a more complex device, such as a modern switching power supply. This power supply uses a variety of capacitor types, including electrolytic, ceramic, and film capacitors. Using a GME ESR-200, you can select the appropriate capacitor type and test frequency for each capacitor, ensuring accurate ESR readings. The GME ESR-300 would be particularly useful in this scenario, thanks to its high accuracy and resolution. You could use the Bluetooth connectivity to log the ESR readings and track the performance of the capacitors over time, allowing you to proactively identify potential failures before they occur. These scenarios illustrate the importance of choosing the right GME professional ESR meter for your specific needs.
Tips for Using Your GME Professional In-Circuit ESR Meter Effectively
To get the most out of your GME professional in-circuit ESR meter, follow these tips: Ensure accurate readings by starting with proper calibration. Always calibrate your meter before each use, following the manufacturer’s instructions. This will compensate for any drift in the meter’s internal components and ensure accurate ESR readings. Clean the probes regularly. Dirty or corroded probes can introduce resistance, leading to inaccurate measurements. Clean the probes regularly with a soft cloth or cotton swab. Use the correct measurement range. Select the appropriate measurement range for the ESR value you expect to measure. Using a range that is too high or too low can result in inaccurate readings. If you’re unsure of the expected ESR value, start with the highest range and gradually decrease it until you get a stable reading.
Minimize lead length. Long probe leads can introduce inductance and resistance, affecting the accuracy of the ESR measurement. Keep the probe leads as short as possible. Avoid touching the capacitor leads or the PCB traces with your fingers while taking measurements. Your body can act as an antenna, introducing noise and interference that can affect the ESR reading. Use shielded probe cables. Shielded probe cables help to minimize noise and interference, especially in electrically noisy environments. Ensure that the shield is properly grounded to the meter’s chassis. Understand the limitations of in-circuit testing. While in-circuit testing is convenient, it’s important to understand its limitations. Other components in the circuit can affect the ESR reading. In some cases, it may be necessary to desolder the capacitor to get an accurate ESR measurement. Consult the datasheet for the capacitor you’re testing. The datasheet will provide the expected ESR value for the capacitor. This will help you to interpret the ESR reading and determine whether the capacitor is within specification. If you’re unsure of the expected ESR value, consult a reputable online resource or forum. There are many online communities where electronics enthusiasts and professionals share their knowledge and experience. Practice makes perfect. The more you use your GME professional ESR meter, the better you’ll become at interpreting ESR readings and diagnosing capacitor failures. This will improve your ability to perform gme parts diagnostics, ultimately saving you time and money in the long run.
Consider environmental factors. Temperature can affect ESR measurements, particularly with electrolytic capacitors. Extreme temperatures can skew readings. Ensure the environment in which you are testing is within a reasonable temperature range, ideally around 20-25°C (room temperature). Also, humidity can impact readings, so avoid testing in very humid environments if possible. Store your GME professional ESR meter properly when not in use. Keep it in a dry, clean place, away from extreme temperatures and humidity. This will help to prolong its lifespan and ensure accurate measurements for years to come. By following these tips, you can maximize the effectiveness of your GME professional in-circuit ESR meter and improve your ability to diagnose and repair electronic circuits efficiently and accurately. Ultimately, finding the best gme tool is about aligning your budget, skill level and project requirements to achieve the best result.
FAQ
What is ESR and why is it important for capacitors?
ESR, or Equivalent Series Resistance, is the measure of internal resistance within a capacitor. Ideally, a capacitor should only have capacitive reactance, meaning it should store and release energy without any loss. However, due to the materials and construction of real-world capacitors, there’s always some inherent resistance. This resistance is what we call ESR. A low ESR value indicates a healthy capacitor that can efficiently store and discharge energy. As a capacitor ages or degrades, its ESR increases. This increased ESR can lead to various problems in electronic circuits, such as reduced performance, increased heat dissipation, and even complete circuit failure. Therefore, monitoring and ensuring low ESR is crucial for maintaining the stability and efficiency of electronic devices.
What are the advantages of in-circuit ESR testing compared to out-of-circuit testing?
In-circuit ESR testing offers several advantages over out-of-circuit testing. First and foremost, it eliminates the need to desolder components, saving valuable time and reducing the risk of damage to the PCB and surrounding components. Desoldering can be a delicate process, and there’s always a chance of lifting pads or traces, especially on older or more fragile boards. Second, in-circuit testing allows you to assess the capacitor’s ESR under its normal operating conditions. This provides a more realistic and reliable indication of its health because the ESR can be affected by the surrounding circuitry. Finally, in-circuit testing is often faster and more convenient, especially when dealing with a large number of capacitors on a densely populated board. You can quickly probe the capacitors and identify any that have high ESR without having to remove them from the circuit.
How do I choose the right GME professional ESR meter for my needs?
Choosing the right GME professional ESR meter depends on your specific needs and budget. Consider the following factors:
* **Accuracy and Resolution:** If you need to measure very small changes in ESR or work on critical applications, choose a meter with high accuracy and resolution.
* **Test Frequency:** Ensure the meter operates at a frequency suitable for the types of capacitors you’ll be testing most frequently. 100kHz is generally good for electrolytic capacitors.
* **In-Circuit Testing Capability:** Make sure the meter is designed for in-circuit testing and uses a low test voltage to avoid turning on semiconductors.
* **User-Friendliness:** Look for a meter with a clear display, intuitive controls, and features such as auto-ranging and data hold.
* **Durability:** Choose a meter with a rugged enclosure and robust construction to withstand daily use.
What is a “good” ESR value for a capacitor?
A “good” ESR value for a capacitor depends on several factors, including the capacitor’s capacitance, voltage rating, type (e.g., electrolytic, ceramic, film), and operating frequency. Generally, smaller capacitance and higher voltage ratings will have lower ESR. Electrolytic capacitors tend to have higher ESR values than ceramic or film capacitors. To determine whether a capacitor’s ESR is within specification, consult the capacitor’s datasheet, which should provide the expected ESR value. If you don’t have the datasheet, you can consult online resources or forums for typical ESR values for different capacitor types and capacitance values. However, always remember that these are just guidelines, and the actual ESR value may vary depending on the specific capacitor.
Can a GME professional ESR meter be used to test other components besides capacitors?
While GME professional ESR meters are primarily designed for testing capacitors, they can sometimes provide useful information about other components as well. For example, a high ESR reading across a coil or inductor might indicate a shorted turn or damaged insulation. Similarly, a high ESR reading across a resistor might indicate that the resistor is failing or has been subjected to excessive heat. However, it’s important to note that an ESR meter is not a substitute for a dedicated multimeter or component tester. These specialized tools are designed to measure specific parameters such as resistance, inductance, and capacitance with greater accuracy and precision. Use the ESR meter to gain some clues, then use other tools for more specific fault finding.
What safety precautions should I take when using a GME professional ESR meter?
When using a GME professional ESR meter, it’s important to take the following safety precautions: Ensure that the circuit under test is de-energized before making any measurements. Never use an ESR meter on a live circuit, as this could damage the meter or pose a safety hazard. Be careful when probing components on a PCB. Avoid shorting components together with the probe tips. Wear appropriate safety glasses to protect your eyes from potential hazards such as flying debris. If you’re working on high-voltage circuits, take extra precautions to avoid electric shock. Use insulated tools and wear appropriate protective gear. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for using the ESR meter.
How often should I calibrate my GME professional ESR meter?
The frequency of calibration depends on several factors, including the meter’s accuracy specifications, the environment in which it’s used, and the frequency of use. As a general rule, it’s a good idea to calibrate your GME professional ESR meter before each use. This will ensure that the meter is providing accurate readings and compensate for any drift in its internal components. If you use the meter frequently or in harsh environments, you may need to calibrate it more often. Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for specific calibration recommendations. Many GME ESR meters have a self-calibration function, which makes it easy to calibrate the meter quickly and easily. However, it’s also a good idea to periodically have the meter professionally calibrated to ensure its accuracy. In short, when working with sensitive and expensive electronic equipment, the GME professional esr tool becomes a necessity.
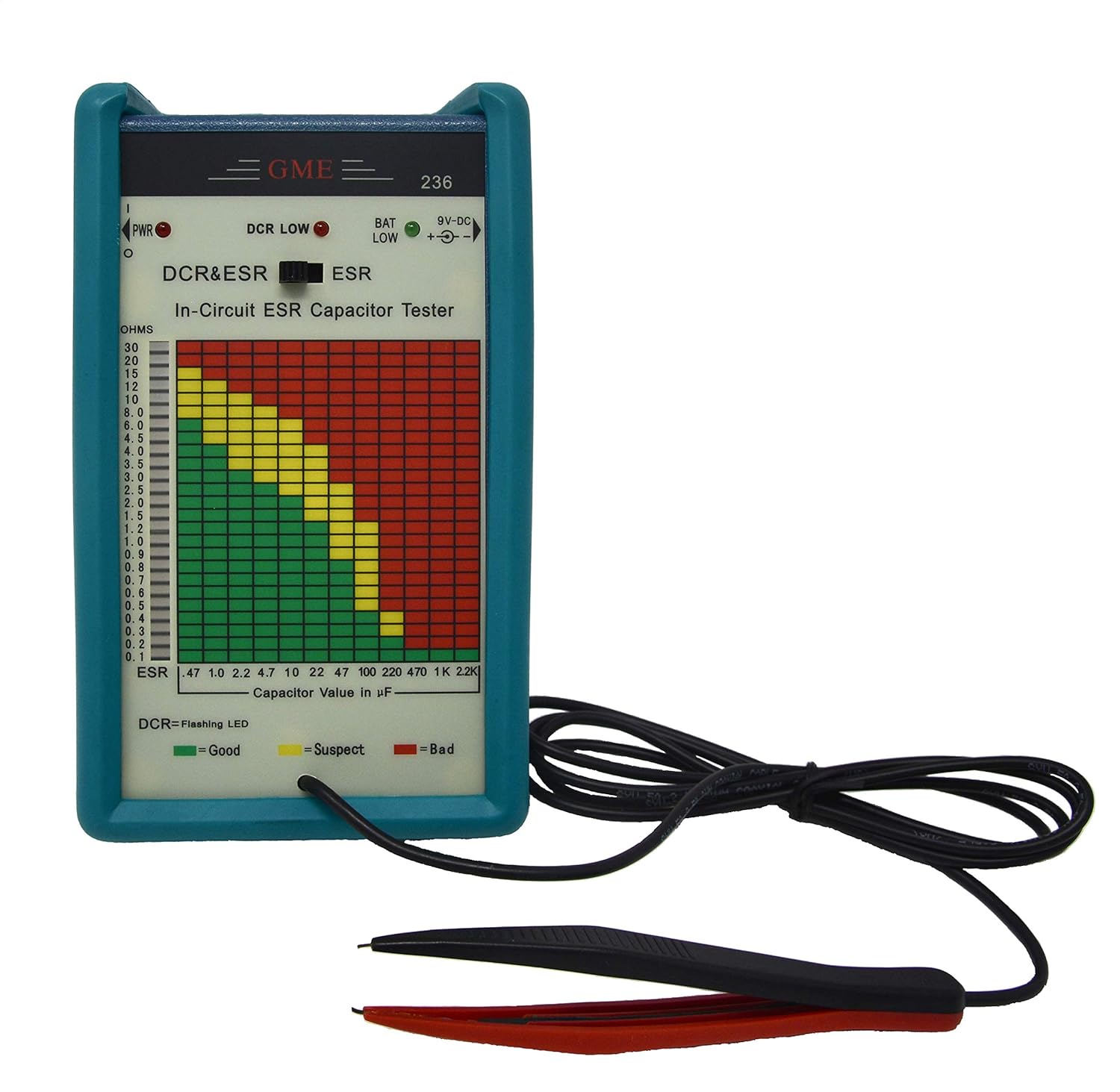
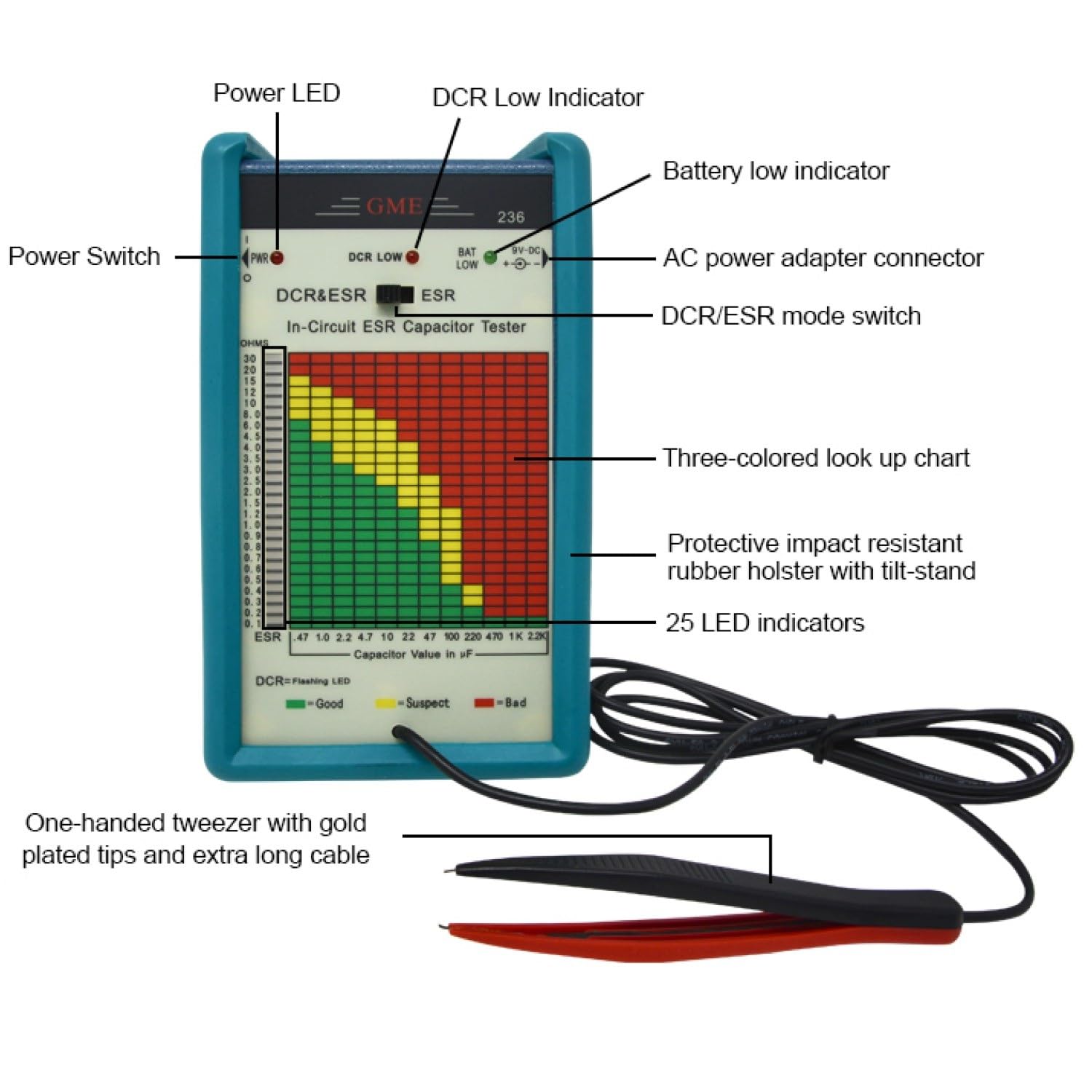






Price: $769.00 - $129.88
(as of Sep 10, 2025 08:35:24 UTC – Details)




