(4-Pack) 3/4″ Bearings Carbon Steel – ID Review wheel bearing – Oemiu
(4-Pack) 3/4″ Bearings Carbon Steel – ID Review: Smooth Rolling & Durable
The relentless pursuit of smooth motion and reliable performance leads many to scrutinize even the smallest components of their machines and contraptions. Wheel bearings, often unassuming in appearance, are pivotal in ensuring efficiency and longevity in countless applications, from simple skateboards to complex industrial machinery. When selecting these crucial components, material choice, dimensions, and build quality become paramount. This comprehensive review focuses on a 4-pack of 3/4″ carbon steel bearings, exploring their potential applications, strengths, weaknesses, and overall suitability for various projects. We’ll delve into the specifics of what makes these bearings tick, offering insights into their design, performance expectations, and how they stack up against alternative options. Understanding the nuances of these small but mighty components can make a significant difference in your project’s success.
Understanding the Anatomy of a Wheel Bearing
Before diving into the specifics of this particular 4-pack of bearings, it’s beneficial to understand the fundamental components and characteristics that define a typical wheel bearing. A bearing, at its core, is designed to reduce friction between moving parts, enabling smooth and efficient rotation. The most common type is the ball bearing, which consists of several key elements. Firstly, there’s the inner race, which is the part that fits around the axle or shaft. This inner race is designed to rotate along with the axle. Secondly, there’s the outer race, which sits stationary within the housing or wheel hub. The rolling elements, in this case, steel balls, reside between the inner and outer races, facilitating smooth movement. A cage or retainer separates and evenly spaces the balls, preventing them from rubbing against each other and ensuring consistent performance. Finally, seals are often incorporated to protect the bearing from contaminants like dirt, dust, and moisture, which can significantly reduce its lifespan and performance. The quality of each of these components, along with the precision of their manufacturing, directly impacts the bearing’s overall performance, durability, and ability to withstand various operating conditions.
The choice of material is also crucial. Carbon steel, as used in these bearings, offers a good balance of strength, hardness, and cost-effectiveness. It’s a common choice for general-purpose bearings where extreme corrosion resistance or exceptionally high speeds are not primary concerns. However, it’s important to consider the specific grade and treatment of the carbon steel, as these factors influence its ability to resist wear and tear. While stainless steel bearings offer superior corrosion resistance, they often come at a higher price point. Similarly, ceramic bearings provide even lower friction and higher speed capabilities, but they are typically reserved for specialized applications. Therefore, understanding the intended use case is critical in determining the optimal bearing material. The 3/4″ inner diameter *wheel bearing* size is also quite popular across a few applications so it is easily sourced.
Examining the (4-Pack) 3/4″ Carbon Steel Bearing Set
Now, let’s focus on the specific 4-pack of 3/4″ carbon steel bearings under review. The 3/4″ dimension refers to the inner diameter (ID) of the bearing, meaning it’s designed to fit a 3/4″ axle or shaft. This particular size is commonly used in various applications, including go-karts, lawnmowers, small trailers, and even some types of skateboards and scooters. The fact that they are sold in a 4-pack suggests they are intended for applications where multiple bearings are required, such as supporting both sides of a wheel or axle. The carbon steel construction indicates a focus on strength and affordability. However, it also implies a potential need for proper lubrication and protection from the elements to prevent rust and corrosion, especially in outdoor or wet environments. The quality of the carbon steel used will greatly determine the bearing’s ability to withstand loads and impacts, as well as its overall lifespan. A higher grade of carbon steel, properly heat-treated, will generally offer superior performance compared to a lower grade.
When assessing these bearings, it’s essential to consider the manufacturing tolerances. Tight tolerances ensure a precise fit and smooth operation, minimizing vibration and noise. Look for indications of precision grinding and finishing, which contribute to a consistent and reliable performance. The type of seal used, if any, is also an important factor. Seals help to keep out contaminants and retain lubricant, extending the bearing’s lifespan. Common seal types include rubber seals (RS) and metal shields (ZZ). Rubber seals offer better protection against contaminants but can create slightly more friction than metal shields. Metal shields provide less protection but allow for higher speeds. Carefully inspect the seals for any signs of damage or defects. A damaged or poorly installed seal can compromise the bearing’s ability to protect itself from the environment. Ultimately, the overall value of this 4-pack of 3/4″ carbon steel bearings depends on a combination of factors, including the quality of materials, manufacturing precision, and intended application. This *3/4″ carbon steel bearing* is a great start, but its long-term functionality will rely on its specific build.
Applications and Use Cases for 3/4″ Bearings
The versatility of 3/4″ bearings makes them suitable for a wide range of applications. As previously mentioned, they are commonly found in go-karts, providing essential support for the axles and ensuring smooth wheel rotation. In lawnmowers, these bearings can be used in the wheels, blade spindles, and other rotating components. Their ability to withstand moderate loads and speeds makes them a practical choice for these applications. Small trailers, such as utility trailers or boat trailers, also often utilize 3/4″ bearings in their wheel hubs. In these scenarios, it’s crucial to ensure that the bearings are properly greased and maintained to prevent premature failure, especially when exposed to water or other harsh conditions. Even some skateboards and scooters employ 3/4″ bearings, although smaller sizes like 8mm are more common in high-performance models. In DIY projects, 3/4″ bearings can be incorporated into custom-built carts, dollies, and other wheeled contraptions. Their availability and relatively low cost make them an attractive option for hobbyists and makers.
Beyond these common applications, 3/4″ bearings can also be found in certain types of industrial machinery, such as conveyor systems and small-scale manufacturing equipment. In these environments, the bearings are often subjected to continuous operation and varying load conditions. Therefore, it’s essential to select bearings that are specifically designed for industrial use, with appropriate lubrication and sealing to ensure long-term reliability. When choosing 3/4″ bearings for any application, it’s critical to consider the specific requirements of the task at hand. Factors such as load capacity, speed, operating temperature, and environmental conditions should all be taken into account. Selecting the wrong type of bearing can lead to premature failure, increased downtime, and potential safety hazards. For demanding applications, it may be worth investing in higher-quality bearings made from more durable materials, such as stainless steel or ceramic. Alternatively, consider *precision 3/4 inch ball bearings* for tighter tolerances. Proper installation and maintenance are also crucial for maximizing the lifespan and performance of any bearing.
Comparing Carbon Steel Bearings to Other Materials
Carbon steel bearings offer a compelling blend of strength, affordability, and versatility, making them a popular choice for a wide range of applications. However, it’s important to understand how they compare to bearings made from other materials, such as stainless steel and ceramic, to make an informed decision for your specific needs. Stainless steel bearings excel in corrosive environments, such as those involving exposure to water, chemicals, or saltwater. The chromium content in stainless steel forms a protective layer that resists rust and corrosion, making these bearings ideal for marine applications, food processing equipment, and medical devices. However, stainless steel bearings typically come at a higher cost than carbon steel bearings, and their load capacity and hardness may be slightly lower.
Ceramic bearings represent the high-end of the bearing spectrum, offering exceptional performance in demanding applications. Ceramic materials, such as silicon nitride (Si3N4) and zirconium dioxide (ZrO2), are incredibly hard, lightweight, and resistant to heat and corrosion. Ceramic bearings exhibit significantly lower friction than steel bearings, allowing for higher speeds and reduced energy consumption. They are also non-magnetic and electrically insulating, making them suitable for specialized applications in aerospace, racing, and high-speed machinery. However, ceramic bearings are considerably more expensive than steel bearings and may not be necessary for general-purpose applications. In addition to these common materials, bearings can also be made from plastic, bronze, or other specialized alloys, each offering unique properties and trade-offs. Plastic bearings are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and can operate without lubrication, making them suitable for low-load applications. Bronze bearings are often used in situations where high loads and low speeds are present. Ultimately, the best material choice depends on the specific requirements of the application, taking into account factors such as cost, performance, and environmental conditions. Consider a *durable 3/4 inch bearing* if you’re not sure which way to go.
| Material | Pros | Cons | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Strong, affordable, versatile | Prone to corrosion, requires lubrication | Go-karts, lawnmowers, trailers, general-purpose machinery |
| Stainless Steel | Excellent corrosion resistance | More expensive than carbon steel, slightly lower load capacity | Marine applications, food processing equipment, medical devices |
| Ceramic | Very low friction, high speed capability, heat and corrosion resistant | Most expensive, may not be necessary for general-purpose applications | Aerospace, racing, high-speed machinery |
Tips for Installation and Maintenance of 3/4″ Bearings
Proper installation and maintenance are crucial for maximizing the lifespan and performance of any bearing, including the 3/4″ carbon steel bearings discussed in this review. Before installing the bearings, ensure that the surfaces they will be mounted on are clean and free of any debris, rust, or burrs. This will help to ensure a proper fit and prevent premature wear. Use appropriate tools to install the bearings, such as a bearing press or a soft-faced hammer. Avoid using excessive force, as this can damage the bearing or the surrounding components. When pressing the bearing into place, apply pressure evenly to the outer race to avoid damaging the inner race or rolling elements. After installation, lubricate the bearings with a high-quality grease or oil that is appropriate for the application. The type of lubricant will depend on factors such as operating temperature, load, and speed. Regularly inspect the bearings for signs of wear, damage, or contamination. Look for any unusual noises, vibrations, or looseness. If you notice any of these issues, replace the bearings immediately to prevent further damage or potential safety hazards.
For bearings that are exposed to harsh environments, such as water or dirt, consider using sealed bearings with rubber seals. These seals will help to keep out contaminants and retain lubricant, extending the bearing’s lifespan. Regularly clean and re-grease the bearings as needed, following the manufacturer’s recommendations. When cleaning the bearings, use a solvent that is compatible with the bearing materials and lubricant. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners, as these can damage the bearing surfaces. After cleaning, thoroughly dry the bearings before re-greasing them. When re-greasing the bearings, use a grease gun to apply the lubricant evenly to all of the rolling elements. Avoid over-greasing the bearings, as this can create excessive pressure and lead to premature failure. Finally, always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for installation, lubrication, and maintenance. By following these tips, you can help to ensure that your 3/4″ bearings provide long-lasting and reliable performance. A proper *maintenance of 3/4 inch bearings* is crucial for overall machine longevity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key specifications I should look for when buying 3/4″ bearings?
When purchasing 3/4″ bearings, several key specifications should be considered to ensure they meet your application’s needs. First and foremost, confirm the inner diameter (ID) is indeed 3/4″, ensuring a proper fit on your axle or shaft. Next, examine the material composition. Carbon steel is common, but consider stainless steel for corrosion resistance or ceramic for high-speed applications. Check the load rating, which indicates the maximum weight the bearing can safely support. Look at the ABEC rating (Annular Bearing Engineering Committee), a measure of manufacturing tolerances; higher ABEC ratings indicate greater precision. Finally, consider the type of seal (rubber seals for better protection, metal shields for higher speeds) and the type of lubricant used, as these factors impact bearing performance and longevity.
What is the difference between open, shielded, and sealed bearings?
The primary difference between open, shielded, and sealed bearings lies in the level of protection they offer against contaminants. Open bearings have no shields or seals, making them easy to lubricate but highly susceptible to dirt, dust, and moisture. They are typically used in clean environments where frequent maintenance is possible. Shielded bearings have metal shields on one or both sides, providing some protection against contaminants while still allowing for relatively easy lubrication. They are a good compromise for applications where moderate contamination is expected. Sealed bearings have rubber or plastic seals that provide the best protection against contaminants, preventing them from entering the bearing and damaging the rolling elements. They are ideal for harsh environments but may generate slightly more friction than shielded or open bearings.
How often should I lubricate my 3/4″ carbon steel bearings?
The frequency of lubrication for your 3/4″ carbon steel bearings depends on several factors, including the application, operating conditions, and type of lubricant used. In general, bearings that are subjected to high loads, high speeds, or harsh environments will require more frequent lubrication than those that operate under milder conditions. As a starting point, consider lubricating your bearings every 3 to 6 months for general-purpose applications. However, for more demanding applications, you may need to lubricate them more frequently, perhaps every month or even weekly. Regularly inspect your bearings for signs of dryness or contamination, and lubricate them whenever necessary. Always use a high-quality grease or oil that is specifically designed for bearings, and follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication frequency and quantity. Over-lubrication can be as detrimental as under-lubrication, so avoid applying excessive amounts of grease or oil.
Can I use WD-40 to lubricate my 3/4″ bearings?
While WD-40 is a versatile product, it is not recommended as a primary lubricant for 3/4″ bearings. WD-40 is primarily a solvent and water displacer, and while it can provide some temporary lubrication, it will not provide the long-lasting protection that bearings require. WD-40 evaporates relatively quickly, leaving the bearing vulnerable to wear and corrosion. Furthermore, WD-40 can dissolve existing grease and wash it away, further reducing lubrication. For proper bearing lubrication, use a dedicated bearing grease or oil that is specifically designed to reduce friction and protect against wear. These lubricants are typically thicker and more viscous than WD-40, providing a longer-lasting protective film. If you use WD-40 to clean your bearings, be sure to thoroughly re-lubricate them with a proper bearing lubricant afterwards.
Are all 3/4″ bearings the same size externally?
No, not all 3/4″ bearings have the same external dimensions. While the inner diameter (ID) will always be 3/4″ to fit a 3/4″ axle or shaft, the outer diameter (OD) and width can vary depending on the specific bearing design and intended application. Different bearing manufacturers may also have slightly different tolerances. It’s essential to consult the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure that the bearing you are purchasing is compatible with your application. Using a bearing with the wrong OD or width can lead to improper fit, increased stress on the bearing and surrounding components, and premature failure. When replacing an existing bearing, it’s always best to measure the dimensions of the old bearing and match them as closely as possible. If you are unsure about the correct bearing size, consult a bearing specialist or refer to a bearing interchange chart.
What does the ABEC rating of a bearing mean?
The ABEC (Annular Bearing Engineering Committee) rating is a system for classifying the manufacturing tolerances of bearings. The ratings range from ABEC 1 to ABEC 9, with higher numbers indicating tighter tolerances and greater precision. A higher ABEC rating generally means that the bearing is more accurate and can rotate more smoothly and efficiently. However, a higher ABEC rating does not necessarily mean that the bearing is more durable or can withstand higher loads. ABEC ratings primarily focus on dimensional accuracy and do not address factors such as material quality, hardness, or load capacity. For most general-purpose applications, an ABEC 1 or ABEC 3 bearing is sufficient. Higher ABEC ratings are typically only necessary for applications that require high speeds, low friction, or precise positioning, such as precision instruments, robotics, and high-speed machinery.
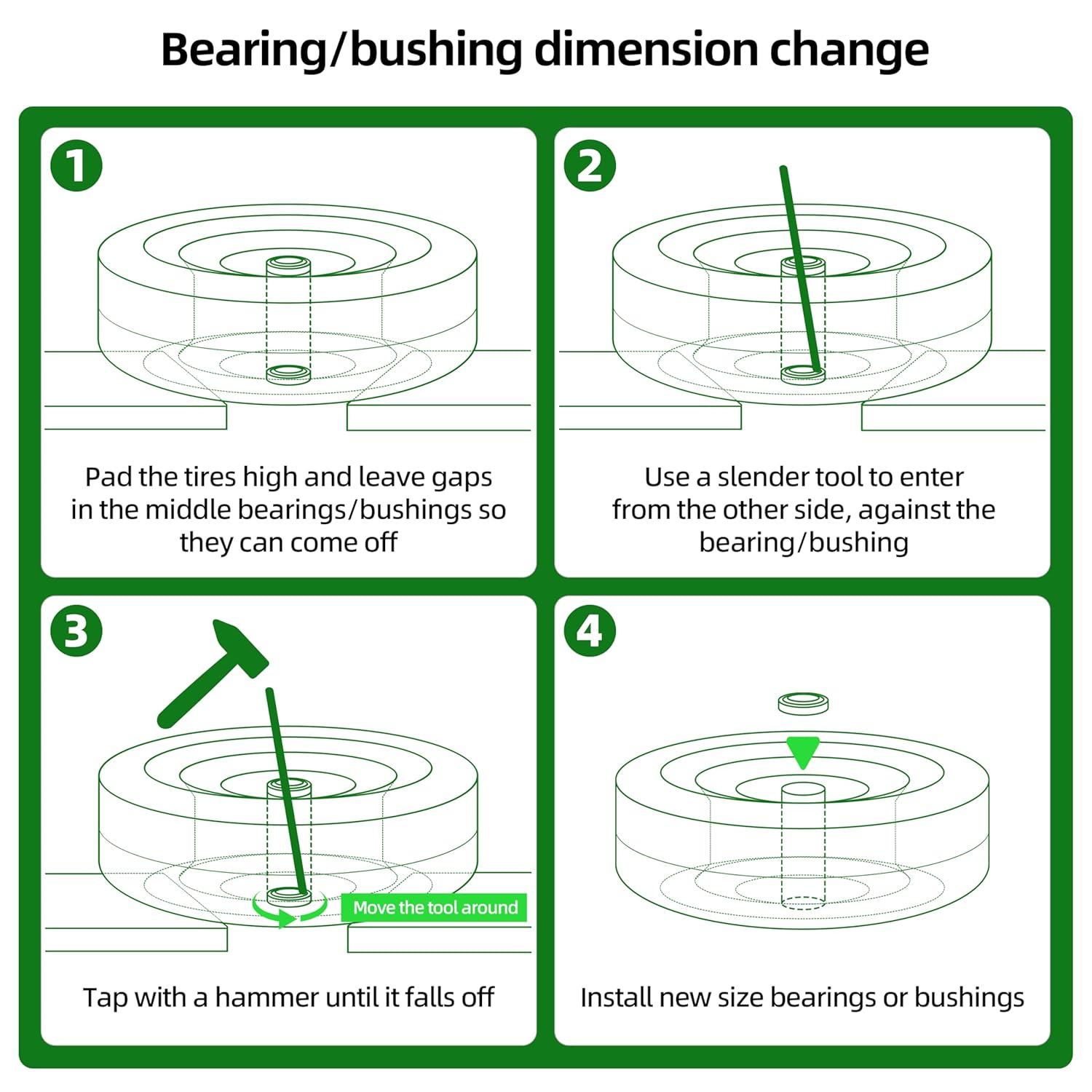
How do I remove a 3/4″ bearing that is stuck?
Removing a stuck 3/4″ bearing can be challenging, but with the right tools and techniques, it can be done safely and effectively. First, try applying penetrating oil to the area around the bearing to help loosen any rust or corrosion. Allow the oil to soak in for several hours or even overnight. Next, use a bearing puller or a bearing separator to grip the bearing securely. A bearing puller is designed to apply even pressure to the bearing without damaging it. If a bearing puller is not available, you can try using a punch and hammer to gently tap the bearing out from behind. Be careful not to damage the surrounding components. Apply heat to the area around the bearing to help expand the metal and loosen the grip. A heat gun or propane torch can be used for this purpose, but be careful not to overheat the bearing or surrounding components. If the bearing is severely stuck, you may need to use a combination of these techniques. As a last resort, you can try cutting the bearing off with a cutting tool, but be extremely careful not to damage the axle or housing. Always wear safety glasses and gloves when removing a stuck bearing.